Fakecalls Android Malware Abuses Legitimate Signing Key

Authored by Dexter Shin
McAfee Mobile Research Team found an Android banking trojan signed with a key used by legitimate apps in South Korea last year. By design, Android requires that all applications must be signed with a key, in other words a keystore, so they can be installed or updated. Because this key can only be used by the developer who created it, an application signed with the same key is assumed to belong to the same developer. That is the case of this Android banking trojan that uses this legitimate signing key to bypass signature-based detection techniques. And these banking trojans weren’t distributed on Google Play or official app stores until now. This threat had been disclosed to the company that owns the legitimate key last year and the company has taken precautions. The company has confirmed that they have replaced the signing key and currently, all their legitimate apps are signed with a new signing key.
Android malware using a legitimate signing key
While tracking the Android banking trojan Fakecalls we found a sample using the same signing key as a well–known app in Korea. This app is developed by a reputable IT services company with extensive businesses across various sectors, including but not limited to IT, gaming, payment, and advertising. We confirmed that most of the malicious samples using this key pretend to be a banking app as they use the same icon as the real banking apps.

Figure 1. Malware and legitimate app on Google Play
Distribution method and latest status
Domains verified last August when we first discovered the samples are now down. However, we investigated URLs related to this malware and we found similar ones related to this threat. Among them, we identified a phishing site that is still alive during our research. The site is also disguised as a banking site.

Figure 2. A phishing page disguised as a Korean banking site
We also found that they updated the domain information of this web page a few days before our investigation.
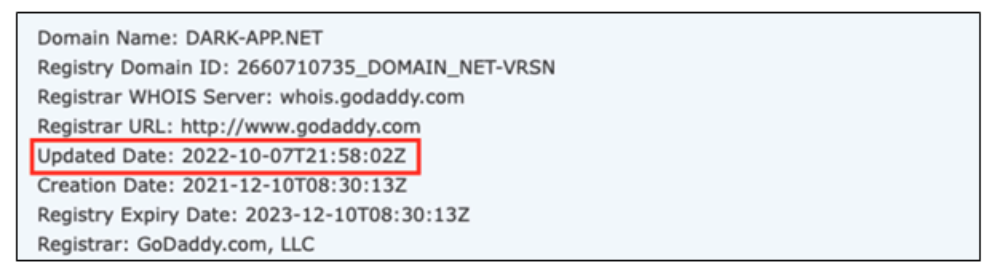
So we took a deeper look into this domain and we found additional unusual IP addresses that led us to the Command and control(C2) server admin pages used by the cybercriminals to control the infected devices.
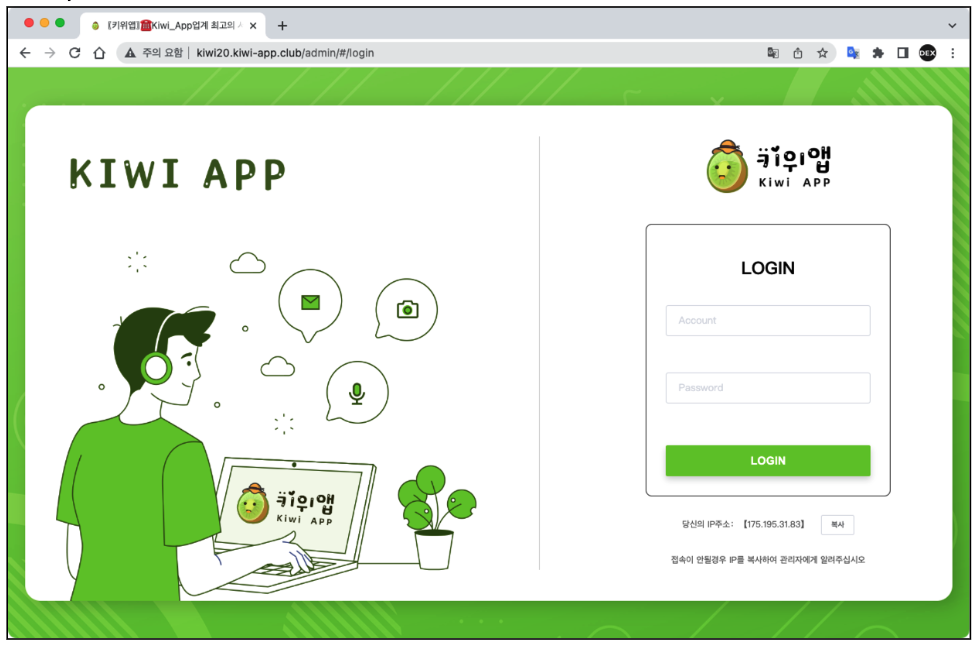
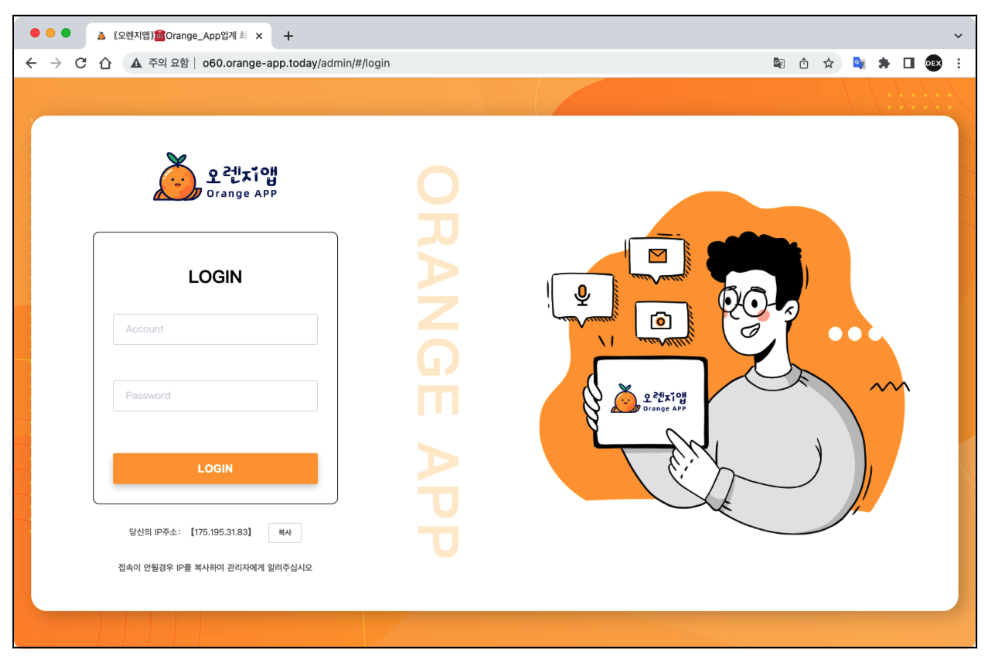
Figure 3. Fakecalls Command and control(C2) admin pages
How does it work
When we check the APK file structure, we can see that this malware uses a packer to avoid analysis and detection. The malicious code is encrypted in one of the files below.
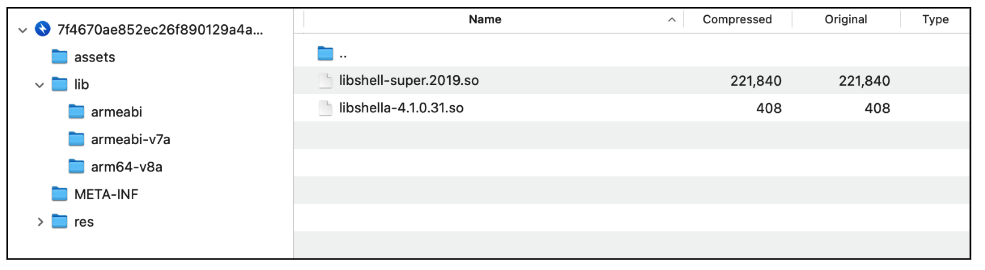
Figure 4. Tencent’s Legu Packer libraries
After decrypting the DEX file, we found some unusual functionality. The code below gets the Android package information from a file with a HTML extension.
 Figure 5. Questionable code in the decrypted DEX file
Figure 5. Questionable code in the decrypted DEX file
This file is in fact another APK (Android Application) rather than a traditional HTML file designed to be displayed in a web browser.
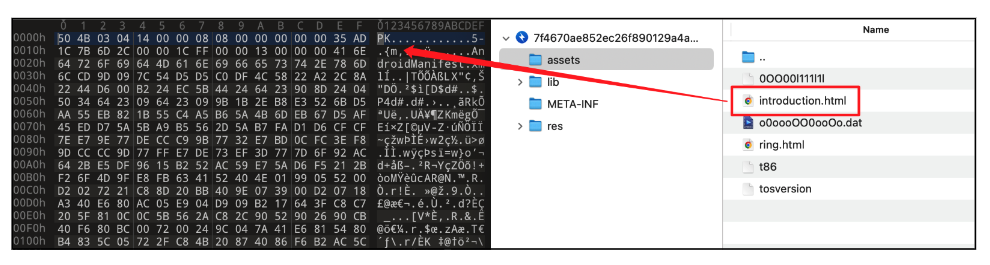 Figure 6. APK file disguised as an HTML file
Figure 6. APK file disguised as an HTML file
When the user launches the malware, it immediately asks for permission to install another app. Then it tries to install an application stored in the “assets” directory as “introduction.html”. The “introduction.html” is an APK file and real malicious behavior happens here.
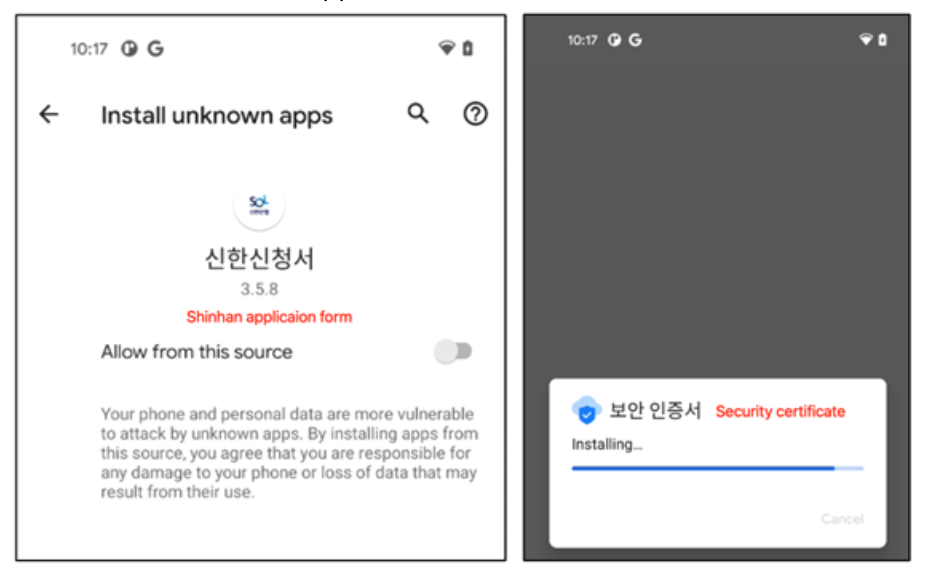
Figure 7. Dropper asks you to install the main payload
When the dropped payload is about to be installed, it asks for several permissions to access sensitive personal information.
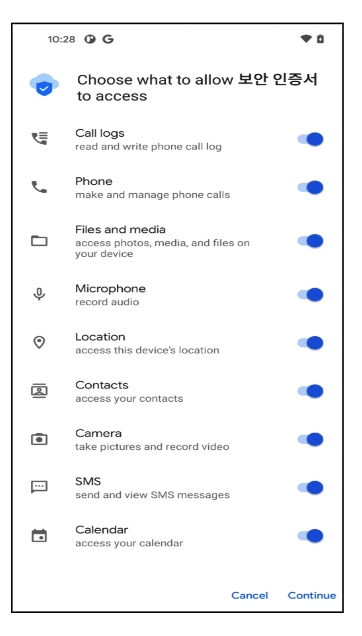
Figure 8. Permissions required by the main malicious application
It also registers several services and receivers to control notifications from the device and to receive commands from a remote Command and Control server.
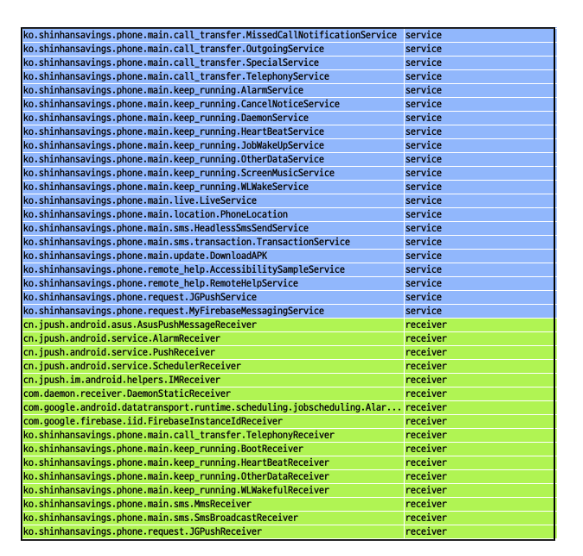
Figure 9. Services and receivers registered by the main payload
By contrast, the malware uses a legitimate push SDK to receive commands from a remote server. Here are the complete list of commands and their purpose.
| Command name | Purpose |
| note | sms message upload |
| incoming_transfer | caller number upload |
| del_phone_record | delete call log |
| zhuanyi | set call forwarding with parameter |
| clear_note | delete sms message |
| assign_zhuanyi | set call forwarding |
| file | file upload |
| lanjie | block sms message from specified numbers |
| allfiles | find all possible files and upload them |
| email_send | send email |
| record_telephone | call recording on |
| inout | re-mapping on C2 server |
| blacklist | register as blacklist |
| listener_num | no function |
| no_listener_num | disable monitoring a specific number |
| rebuild | reset and reconnect with C2 |
| deleteFile | delete file |
| num_address_list | contacts upload |
| addContact | add contacts |
| all_address_list | call record upload |
| deleteContact | delete contacts |
| note_intercept | intercept sms message from specified numbers |
| intercept_all_phone | intercept sms message from all |
| clear_date | delete all file |
| clear_phone_contact | delete all contacts |
| clear_phone_record | delete all call log |
| per_note | quick sms message upload |
| soft_name | app name upload |
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving and using new ways to bypass security checks, such as abusing legitimate signing keys. Fortunately, there was no damage to users due to this signing key leak. However, we recommend that users install security software on their devices to respond to these threats. Also, users are recommended to download and use apps from the official app stores.
McAfee Mobile Security detects this threat as Android/Banker regardless of the application, is signed with the previously legitimate signing key.
Indicators of Compromise
| SHA256 | Name | Type |
| 7f4670ae852ec26f890129a4a3d3e95c079f2f289e16f1aa089c86ea7077b3d8 | 신한신청서 | Dropper |
| 9e7c9b04afe839d1b7d7959ad0092524fd4c6b67d1b6e5c2cb07bb67b8465eda | 신한신청서 | Dropper |
| 21ec124012faad074ee1881236c6cde7691e3932276af9d59259df707c68f9dc | 신한신청서 | Dropper |
| 9621d951c8115e1cc4cf7bd1838b8e659c7dea5d338a80e29ca52a8a58812579 | 신한신청서 | Dropper |
| 60f5deb79791d2e8c2799e9af52adca5df66d1304310d1f185cec9163deb37a2 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| 756cffef2dc660a241ed0f52c07134b7ea7419402a89d700dffee4cc6e9d5bb6 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| 6634fdaa22db46a6f231c827106485b8572d066498fc0c39bf8e9beb22c028f6 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| 52021a13e2cd7bead4f338c8342cc933010478a18dfa4275bf999d2bc777dc6b | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| 125772aac026d7783b50a2a7e17e65b9256db5c8585324d34b2e066b13fc9e12 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| a320c0815e09138541e9a03c030f30214c4ebaa9106b25d3a20177b5c0ef38b3 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| c7f32890d6d8c3402601743655f4ac2f7390351046f6d454387c874f5c6fe31f | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| dbc7a29f6e1e91780916be66c5bdaa609371b026d2a8f9a640563b4a47ceaf92 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
| e6c74ef62c0e267d1990d8b4d0a620a7d090bfb38545cc966b5ef5fc8731bc24 | 보안인증서 | Banker |
Domains:
- http[://]o20-app.dark-app.net
- http[://]o20.orange-app.today
- http[://]orange20.orange-app.today
The post Fakecalls Android Malware Abuses Legitimate Signing Key appeared first on McAfee Blog.
